[Ebook Việt Hoá] The Instant Guide to Healthy Houseplants (Hướng dẫn tức thời để chăm cây trong nhà khoẻ mạnh), Chi Polystichum
[Ebook Việt Hoá] The Instant Guide to Healthy Houseplants: Polypodium scolopendria (Wart fern, East Indian polypody)
- Nguồn: [Ebook Việt Hoá] The Instant Guide to Healthy Houseplants (Hướng dẫn tức thời để chăm cây trong nhà khoẻ mạnh)
- Biên tập: Dũng Cá Xinh
- Biên dịch: Team Codai.net
English
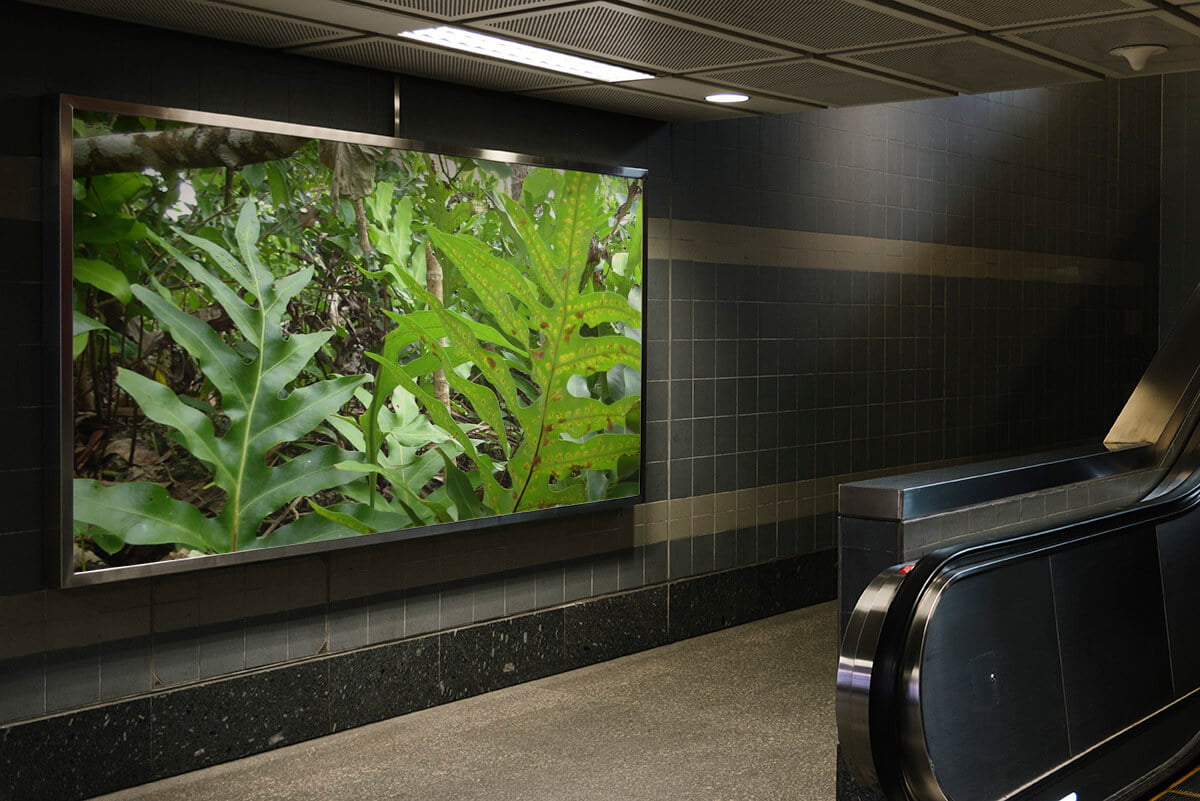
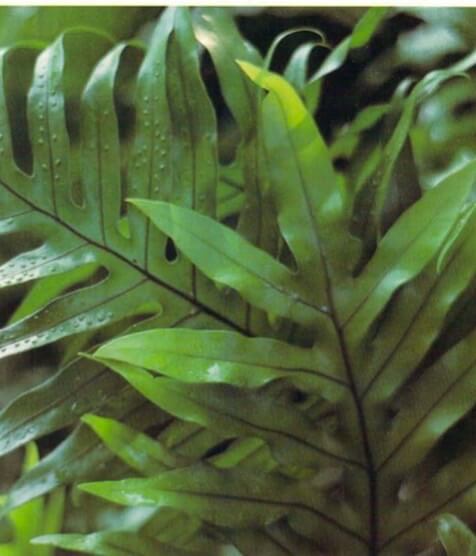
The wart fern, which comes from the Old World tropics, grows well as a garden ground cover in frost-free areas such as Florida and southern California but is also a surprisingly durable indoor plant that can be grown in shallow pots or hanging baskets. The magnificent lobed emerald-green leaves (1-3 feet-30 cm-1 m long) are as shiny as patent leather. The plant gets its common name from round raised spores, said to resemble warts, that appear in irregular rows on the surfaces of mature leaves.

Light
Needs bright light but shade from midday summer sunlight.
Temperature
Maintain an ideal temperature range of 60-80°F (16-27°C) year-round. Plant will not tolerate temperatures below 50°F ( 10°C).
Water
Keep soil uniformly moist, not soggy, by watering 3-4 times a week in summer, 2-3 times a week in fall and winter. If plant is in hanging basket, check soil daily and water whenever soil feels dry.
Humidity
Plant prefers moderate humidity but tolerates low humidity. Mist 4 times a week.
Soil
Use equal parts peat moss and perlite, or use I part peat or leaf mold, I part sand and 2 parts perlite. (Omit sand for plants in hanging baskets,) Osmunda fiber can be used instead of either mix.
Feeding
During the spring and summer, fertilize every 2 weeks with a solution offish emulsion or with a water-soluble fertilizer at half the manufacturer’s recommended strength. Do not feed newly repotted plants until I month after repotting.
Repotting
When roots completely fill pot and rhizomes have spread over the edge, repot in next size container. Add bone meal and composted cow manure (2 tablespoons of each per gallon) to soil mix. Wait I month before feeding.
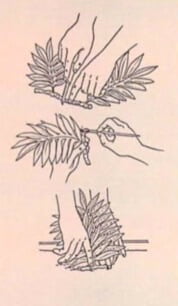
Propagation
By rhizomes (especially for hang- ing baskets)
- 1. Cut rhizomes into 4-in (10- cm) lengths, discarding dead or brown rhizomes and paring down to healthy tissue.
- 2. Dust cut surfaces with hormone rooting powder.
- 3. Repot vigorous green rhizomes with soil just slightly covering the rhizomes. Secure rhizomes with pieces of bent wire.
By division
- 1. With a sharp knife, remove plant from pot and separate plant and roots into 2 equal parts.
2. Repot each section in separate container with soil almost covering the rhizomes. - 3. Pin small rootless pieces of green rhizome to the soil surface with wire.
What Goes Wrong

- Leaves yellow, little or no growth: Too cold, too wet or needs feeding. Maintain a temperature range of 60-80°F (16-27°C). Keep soil evenly moist but not waterlogged by watering when soil surface begins to dry. In spring and summer, fertilize every 2 weeks with a solution of fish emulsion or a water soluble fertilizer at half the manufacturer’s recommended strength. (Do not feed newly repotted plants until I month after repotting.)
- Round wartlike bumps on upper surface of mature fronds; round, tannish dents on undersides of fronds: Natural spore clusters.
- Older leaves turn yellow then brown: Natural aging that usually occurs after spore clusters appear. Remove affected leaves.
- Leaves wrinkled, wilted: Overwatered, underwatered, overfertilized, phytotoxicity from overuse of chemicals or plant potbound. Remove wilted leaves. If soil is wet, remove plant from pot and check roots for damage. If roots are severely damaged, pare down to healthy root tissue and repot in fresh soil. If soil is completely dry, plunge pot in tub of water for 10 minutes, remove and let drain. Flush soil with water if plant has been given overdose of fertilizer or chemical insecticide. Do not use emulsifiable concentrates (chemicals labeled EC) on ferns. Repot in next size pot when roots have completely filled pot and rhizomes have spread over the edge of the pot.
- Round, yellow spots on leaves: Scale insect. Spray with mild soapy water, especially on undersides of leaves. Rinse. Do not use emulsifiable concentrates (chemicals labeled EC) on ferns.
- Small, brown, soft-bodied insects on new growth: Aphid. Spray with mild, soapy water. Rinse. Repeat weekly until clear. Do not use emulsifiable concentration (chemicals labeled EC) on ferns.
- Old fronds partially yellowed, with scorched margins; new fronds shriveled: Humidity too low, temperature too high, sunlight too strong or plant in draft. Increase misting. Group plants together. Place pot in tray of wet gravel or stones. Provide shade from direct midday sunlight and protect plant from drafts.
- Leaves small, yellow- green; some leaves have scorched areas: Too much direct sunlight. Shade plant from midday sunlight or move plant to a spot that gets bright light but not direct sunlight.
Tiếng Việt
Loài dương xỉ này, có nguồn gốc từ vùng nhiệt đới Cựu thế giới, phát triển tốt khi mặt sân vườn phủ kín ở những khu vực không có sương giá như Florida và nam California nhưng cũng là một loại cây trong nhà bền đáng kinh ngạc, có thể trồng trong chậu nông hoặc giỏ treo. Những chiếc lá xanh ngọc lục bảo hình thùy tuyệt đẹp (dài 1-3 foot-30 cm-1 m) sáng bóng như làn da. Loại cây này có tên gọi chung từ các bào tử hình tròn mọc lên, được cho là giống mụn cóc, xuất hiện thành các hàng không đều trên bề mặt của các lá trưởng thành.

Ánh sáng
Cần ánh sáng rực rỡ nhưng thích nghi được từ bóng râm đến ánh nắng giữa trưa mùa hè.
Nhiệt độ
Duy trì khoảng nhiệt độ lý tưởng là 60-80 ° F (16-27 ° C) quanh năm. Cây sẽ không chịu được nhiệt độ dưới 50 ° F (10 ° C).
Nước
Giữ đất ẩm đồng đều, không bị sũng nước bằng cách tưới 3-4 lần một tuần vào mùa hè, 2-3 lần một tuần vào mùa thu và mùa đông. Nếu cây trồng trong giỏ treo, hãy kiểm tra đất hàng ngày và tưới nước bất cứ khi nào thấy đất khô.
Độ ẩm
Cây ưa ẩm vừa phải nhưng vẫn chịu độ ẩm thấp. Phun ẩm 4 lần một tuần.
Đất
Sử dụng rêu than bùn và đá trân châu hai phần bằng nhau hoặc sử dụng một phần than bùn hoặc nấm mốc lá, một phần cát và 2 phần đá trân châu. (Không bỏ cát cho cây trồng trong giỏ treo), có thể sử dụng sợi Osmunda thay cho một trong hai loại hỗn hợp.
Bón phân
Trong mùa xuân và mùa hè, bón phân 2 tuần một lần bằng đạm cá hoặc phân bón hòa tan trong nước với nồng độ một nửa khuyến cáo của nhà sản xuất. Không cho cây mới thay chậu cho đến 1 tháng sau khi thay chậu.
Thay chậu
Khi rễ hoàn toàn lấp đầy chậu và thân rễ đã lan ra rìa, hãy thay vào chậu lớn hơn. Thêm bột xương và phân bò ủ hoai (2 muỗng canh mỗi loại cho mỗi gallon) vào hỗn hợp đất. Chờ một tháng trước khi bón phân.
Nhân giống
Bằng thân rễ (đặc biệt để treo giỏ)
- 1. Cắt thân rễ thành các đoạn dài 4 inch (10 cm), loại bỏ các thân rễ đã chết hoặc màu nâu và cắt theo mô khỏe mạnh.
- 2. Phủ lên bề mặt cắt lớp bột kích tố ra rễ.
- 3. Thay thế những thân rễ xanh tươi đầy sức sống bằng đất và chỉ phủ một chút lên thân rễ. Giữ chặt thân rễ bằng các đoạn dây uốn cong.
Bằng cách phân chia
- 1. Dùng dao sắc lấy cây ra khỏi chậu, tách cây và rễ thành 2 phần bằng nhau.
- 2. Thay từng phần trong thùng riêng biệt với đất gần như phủ kín thân rễ.
- 3. Dùng dây kẽm ghim các đoạn thân rễ nhỏ không có rễ lên bề mặt đất.

Những vấn đề có thể xảy ra

- Lá vàng, ít hoặc không mọc: Quá lạnh, quá ẩm ướt hoặc cần bón phân. Duy trì phạm vi nhiệt độ từ 60-80 ° F (16-27 ° C). Giữ đất ẩm đều nhưng không bị úng bằng cách tưới nước khi bề mặt đất bắt đầu khô. Vào mùa xuân và mùa hè, bón phân 2 tuần một lần bằng đạm cá hoặc phân bón hòa tan trong nước với nồng độ một nửa khuyến cáo của nhà sản xuất. (Không cho cây mới thay chậu cho đến 1 tháng sau khi thay chậu.)
- Bướu cây tròn như vết sưng trên bề mặt trên của lá trưởng thành; vết lõm tròn, hơi nâu ở mặt dưới lá: Cụm bào tử tự nhiên.
- Các lá già chuyển sang màu vàng rồi nâu: Sự lão hóa tự nhiên thường xảy ra sau khi các cụm bào tử xuất hiện. Loại bỏ các lá bị ảnh hưởng.
- Lá nhăn nheo, héo úa: Tưới quá nhiều nước, sũng nước, bón quá nhiều, nhiễm độc thực vật do lạm dụng quá nhiều hóa chất hoặc chậu quá chật. Loại bỏ lá héo. Nếu đất ướt, hãy lấy cây ra khỏi chậu và kiểm tra rễ xem có bị hư hại không. Nếu rễ bị tổn thương nghiêm trọng, hãy xén bớt mô rễ khỏe mạnh và thay chậu vào đất mới. Nếu đất khô hoàn toàn, ngâm chậu vào chậu nước trong 10 phút, vớt ra và để cho ráo nước. Rửa sạch đất bằng nước nếu cây bị bón quá liều lượng phân bón hoặc thuốc trừ sâu hóa học. Không sử dụng chất cô đặc nhũ hóa (hóa chất có nhãn EC) trên dương xỉ. Thay vào chậu lớn hơn khi rễ đã lấp đầy chậu và thân rễ đã lan ra mép chậu.
- Các đốm tròn, vàng trên lá: Côn trùng vảy. Xịt bằng nước xà phòng nhẹ, đặc biệt là ở mặt dưới của lá. Rửa sạch. Không sử dụng chất cô đặc nhũ hóa (hóa chất có nhãn EC) trên dương xỉ.
- Côn trùng nhỏ, màu nâu, thân mềm đang phát triển: Rệp. Xịt bằng nước xà phòng nhẹ. Rửa sạch. Lặp lại hàng tuần cho đến khi hết. Không sử dụng chất cô đặc nhũ hóa (hóa chất có nhãn EC) trên dương xỉ.
- Lá già bị vàng một phần, mép bị cháy xém; lá mới bị héo: Độ ẩm quá thấp, nhiệt độ quá cao, ánh sáng mặt trời quá mạnh hoặc gió lùa. Tăng cường phun sương. Nhóm các cây lại với nhau. Đặt chậu vào khay có sỏi hoặc đá ướt. Che mát cho cây khỏi ánh nắng trực tiếp giữa trưa và bảo vệ cây khỏi gió lùa.
- Lá nhỏ, xanh vàng; một số lá bị cháy xém: Quá nhiều ánh nắng trực tiếp. Che mát cho cây vào giữa trưa hoặc di chuyển cây đến nơi có ánh sáng nhưng không phải ánh nắng trực tiếp.

