Ebook Việt Hoá] Plant parenting: Easy ways to make more houseplants vegetables and flowers - LESLIE F. HALLECK
[Ebook Việt Hoá] Plant parenting – LESLIE F. HALLECK (Nhân giống cây) – HOW SEEDS GERMINATE (Cách hạt nảy mầm)
- Nguồn: [Ebook Việt Hoá] Plant parenting: Easy ways to make more houseplants, vegetables, and flowers – LESLIE F. HALLECK (Nhân giống cây: Những cách dễ nhất để nhân giống cây cảnh trong nhà, rau và hoa)
- Biên tập: Dũng Cá Xinh (Tháng 08/20201)
- Dịch: Huyền Nguyễn
English
Sowing new plants from seed is not only exciting, it’s also an economical way to quickly grow a large quantity of plants. Plus, you’ll be able to grow a much wider variety than if you only buy finished transplants from a garden center or online plant source. If you grow your plants outdoors, starting all your seedlings or cuttings inside can give you a big jump on the growing season.
Simply put, seeds are plants in embryo form. They contain enough energy to germinate and grow a new plant on their own once they are exposed to water and air, as well as the right light and temperature conditions. Until these conditions are met, seeds remain dormant, protected by a seed coat, called a testa, or chemical germination inhibitors. Seed coats prevent water from entering the seed embryo. Chemical inhibitors prevent the seed from germinating under the wrong environmental conditions. Otherwise, seeds would germinate at the wrong time, out of season, or in the wrong location and die. Inhibitors also make it possible for seeds to travel some distance away from the parent plant, which helps plant species spread geographically and improve genetic diversity.
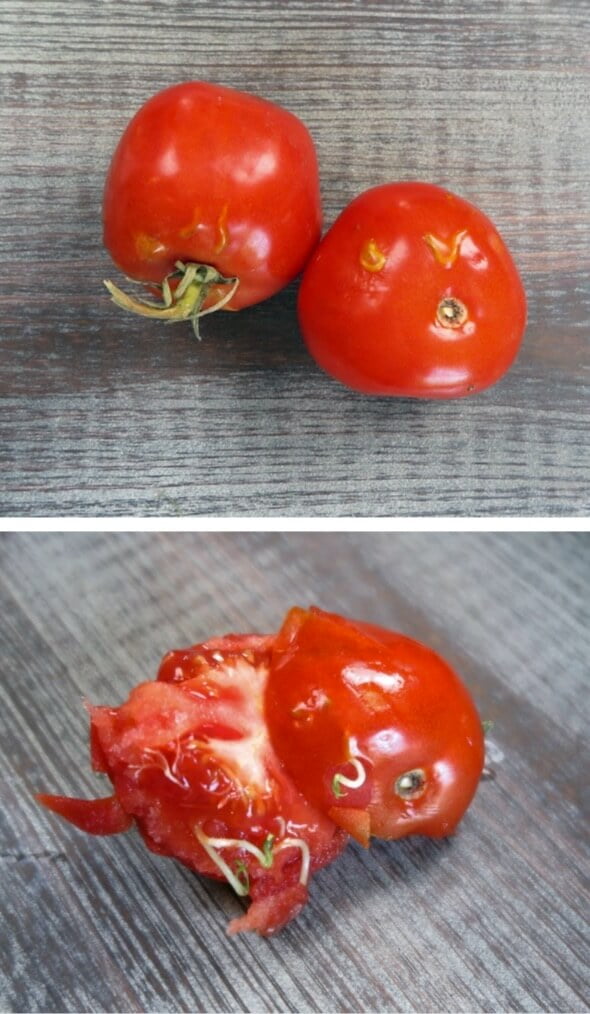
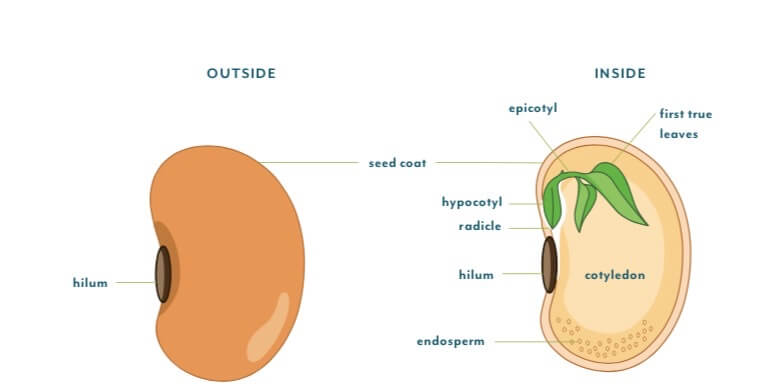
Some seeds have a soft seed coat, while others have a very hard seed coat. Under the seed coat of some seeds, you’ll find another layer called the endosperm, which serves as a food source for the seed. Under the endosperm, you’ll find the seed embryo, which includes the radicle (root initial – the beginnings of new root tissue), the hypocotyl (shoot initial below the seed leaves), one or two cotyledons (seed leaves), and the epicotyl (the stem initial and true leaf initials that will grow above the cotyledon). You’ll often see a small scar or eye on a dry seed. This small area, called the hilum, is where the seed was originally attached to the ovary on the mother plant.
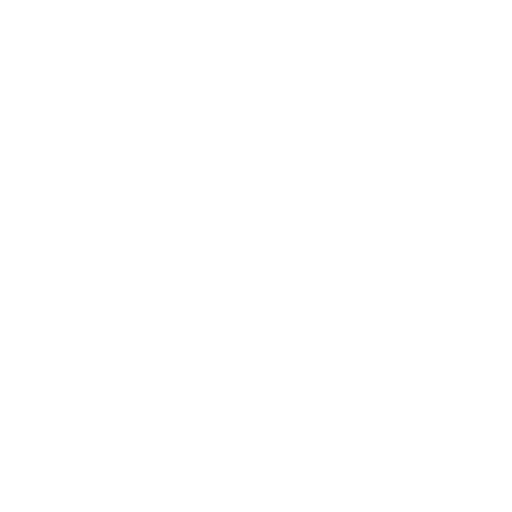
Sometimes chemical germination inhibitors break down and a seed will germinate too early. Have you ever seen a tomato seed sprout inside a tomato fruit? We call this precocious germination, or vivipary. It happens when the hormones that regulate seed development degrade. Once the hormonal germination inhibitor is no longer present, the seeds will germinate, even under the wrong environmental conditions.
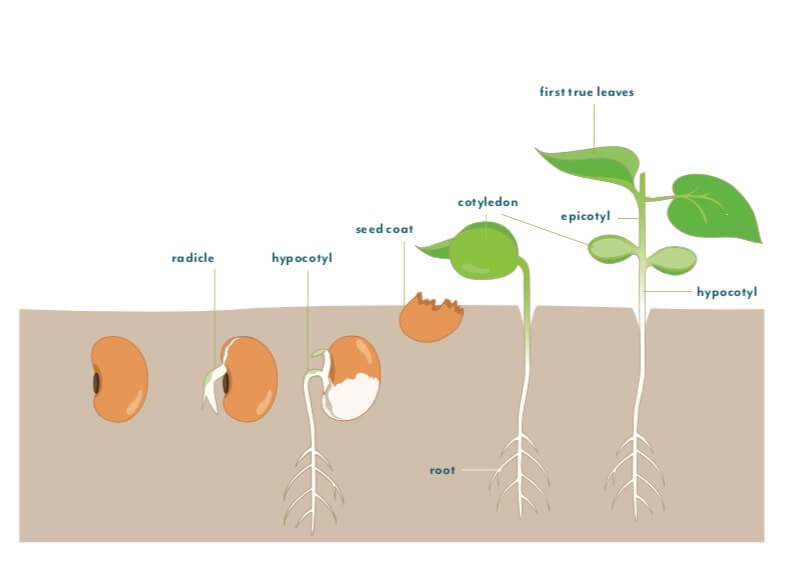
After the seed germinates and the radicle pushes into the soil or water, it will develop a primary root and the cotyledon (seed leaves) will open. Afterward, the first true leaf or leaves unfurl. Once you see the first true leaf emerging, you know your seedling is on its way.


Tiếng Việt
Ươm cây mới từ hạt giống không chỉ thú vị mà còn là một cách tiết kiệm để nhanh chóng trồng một số lượng lớn cây. Ngoài ra, bạn sẽ có thể trồng nhiều loại cây khác nhau so với việc bạn chỉ mua cây giống đã ươm sẵn từ trung tâm vườn hoặc qua các cửa hàng cây trồng trực tuyến. Nếu bạn trồng cây ngoài trời, việc bắt đầu ươm hạt hoặc cành giâm bên trong có thể mang lại cho bạn một bước tiến lớn trong mùa trồng trọt.
Nói một cách đơn giản, hạt giống là thực vật ở dạng phôi. Chúng chứa đủ năng lượng để tự nảy mầm và phát triển một cây mới sau khi được tiếp xúc với nước và không khí, cũng như điều kiện ánh sáng và nhiệt độ thích hợp. Cho đến khi các điều kiện này được đáp ứng, hạt vẫn ở trạng thái không hoạt động, được bảo vệ bởi lớp vỏ hạt, được gọi là testa, hoặc các chất ức chế nảy mầm hóa học. Vỏ hạt ngăn không cho nước xâm nhập vào phôi hạt. Các chất ức chế hóa học ngăn không cho hạt nảy mầm trong các điều kiện môi trường không thích hợp. Nếu không, hạt giống sẽ nảy mầm không đúng thời điểm, trái mùa, và chết. Các chất ức chế cũng làm cho hạt giống có thể di chuyển xa cây mẹ một khoảng cách, điều này giúp các loài thực vật lan rộng về mặt địa lý và cải thiện tính đa dạng di truyền.
Một số loại hạt có vỏ mềm, trong khi những hạt khác có vỏ rất cứng. Dưới lớp vỏ hạt của một số loại hạt, bạn sẽ tìm thấy một lớp khác được gọi là nội nhũ, dùng làm nguồn thức ăn cho hạt. Dưới lớp nội nhũ, bạn sẽ tìm thấy phôi hạt, bao gồm lá mầm (rễ ban đầu, sự khởi đầu của mô rễ mới), hypocotyl (chồi ban đầu bên dưới lá hạt), một hoặc hai lá mầm (lá hạt), và epicotyl (phần đầu của thân và lá thật sẽ mọc phía trên lá mầm). Bạn sẽ thường thấy một vết sẹo nhỏ hoặc mắt trên hạt khô. Khu vực nhỏ này, được gọi là hilum, là nơi hạt ban đầu được gắn trên cây mẹ.
Đôi khi các chất ức chế nảy mầm hóa học phá vỡ hạt và hạt sẽ nảy mầm quá sớm. Bạn đã bao giờ nhìn thấy hạt Cà Chua nảy mầm bên trong quả cà chua chưa? Chúng tôi gọi đây là sự nảy mầm sớm hay còn gọi là vivipary. Hiện tượng này xảy ra khi các hormone điều chỉnh sự phát triển của hạt giống bị suy giảm. Một khi chất ức chế nảy mầm nội tiết không còn, hạt sẽ nảy mầm, ngay cả trong điều kiện môi trường không thích hợp.
Sau khi hạt nảy mầm và rễ mầm bám vào đất hoặc nước, nó sẽ phát triển thành rễ sơ cấp và lá mầm sẽ mở ra. Sau đó, lá thật đầu tiên sẽ xuất hiện. Khi bạn nhìn thấy chiếc lá thật đầu tiên mọc lên, bạn biết rằng cây con của bạn đang trên đà phát triển.




![[Ebook Việt Hoá] Plant parenting – LESLIE F. HALLECK (Nhân giống cây) – HOW SEEDS GERMINATE (Cách hạt nảy mầm) [Ebook Việt Hoá] Plant parenting – LESLIE F. HALLECK (Nhân giống cây) – HOW SEEDS GERMINATE (Cách hạt nảy mầm)](https://vn1.vdrive.vn/codai.net/2021/02/ebook-huong-dan-nhan-giong-cay-canh-rau-va-hoa-04.jpg)


